Part a of the figure shows a type of package
that the chip is provided in, called a dual-inline package (DIP). Part b illustrates
the 7404 chip, which comprises six NOT gates. The chip’s external connections
are called pins or leads. Two pins are used to connect to VDD and
Gnd, and other pins provide connections to the NOT gates.
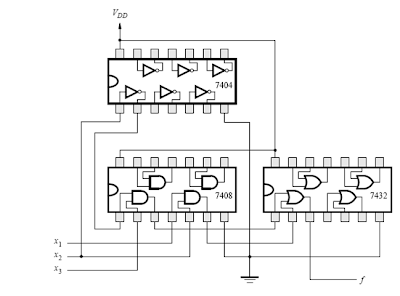
As an example of how a logic
circuit can be implemented using 7400-series chips, consider the function f = x1x2
+ x2’x3. A NOT gate is required to produce x2, as well as
2 two-input AND gates and a two-input OR gate.
An
implementation of f = x1x2
+ x2’x3
The figure shows three 7400-series chips that can
be used to implement the function. We assume that the three input signals x1,
x2, and x3 are produced as outputs by some other
circuitry that can be connected by wires to the three chips.
Because of their low logic capacity, the standard
chips are seldom used in practice today, with one exception. Many modern
products include standard chips that contain buffers. Buffers are logic gates
that are usually used to improve the speed of circuits. An example of a buffer
chip is depicted here:
It is the 74244 chip, which comprises eight tri-state
buffers. We describe how tri-state buffers work later. Rather than showing
how the buffers are arranged inside the chip package, as we did for the NOT, we
show only the pin numbers of the package pins that are connected to the
buffers. The package has 20 pins, and they are numbered in the same manner as
shown for NOT-gates chip; Gnd and VDD connections are provided on
pins 10 and 20, respectively. Many other buffer chips also exist. For example,
the 162244 chip has 16 tri-state buffers. It is part of a family of devices
that are similar to the 7400-series chips but with twice as many gates in each
chip. These chips are available in multiple types of packages, with
the most popular being a small-outline integrated circuit (SOIC) package. An
SOIC package has a similar shape to a DIP, but the SOIC is considerably smaller
in physical size. As integrated circuit technology has improved over time, a
system of classifying chips according to their size has evolved. The earliest
chips produced, such as the 7400-series chips, comprise only a few logic gates.
The technology used to produce these chips is referred to as small-scale
integration (SSI). Chips that include slightly more logic circuitry, typically
about 10 to 100 gates, represent medium-scale integration (MSI). Until the
mid-1980s chips that were too large to qualify as MSI were classified
large-scale integration (LSI). In recent years the concept of classifying
circuits according to their size has become of little practical use. Most
integrated circuits today contain many thousands or millions of transistors.
Regardless of their exact size, these large chips are said to be made with very
large scale integration (VLSI) technology. The trend in digital hardware
products is to integrate as much circuitry as possible onto a single chip. Thus
most of the chips used today are built
with VLSI technology, and the older types of chips are used rarely.


No comments:
Post a Comment